Scrolled windows
Scrolled windows are used to create a scrollable area with another widget inside it. You may insert any type of widget into a scrolled window, and it will be accessible regardless of the size by using the scrollbars.
The function GBin.scrolled_window is used to create a new scrolled window.
val GBin.scrolled_window :
?hadjustment:GData.adjustment ->
?vadjustment:GData.adjustment ->
?hpolicy:Gtk.Tags.policy_type ->
?vpolicy:Gtk.Tags.policy_type ->
?placement:Gtk.Tags.corner_type ->
?shadow_type:Gtk.Tags.shadow_type ->
?border_width:int ->
?width:int ->
?height:int ->
?packing:(GObj.widget -> unit) ->
?show:bool -> unit -> scrolled_windowWhere the argument hadjustment is the adjustment for the horizontal direction, and vadjustment, the adjustment for the vertical direction. These are almost always not given.
method set_hpolicy : Gtk.Tags.policy_type -> unit
method set_vpolicy : Gtk.Tags.policy_type -> unitThis sets the policy to be used with respect to the scrollbars. The set_hpolicy sets the policy for the horizontal scrollbar, and the set_vpolicy for the vertical scrollbar.
The policy may be one of `AUTOMATIC or `ALWAYS. `AUTOMATIC will automatically decide whether you need scrollbars, whereas `ALWAYS will always leave the scrollbars there.
You can then place your object into the scrolled window using the following function.
method add_with_viewport : GObj.widget -> unitHere is a simple example that packs a table with 100 toggle buttons into a scrolled window. I’ve only commented on the parts that may be new to you.
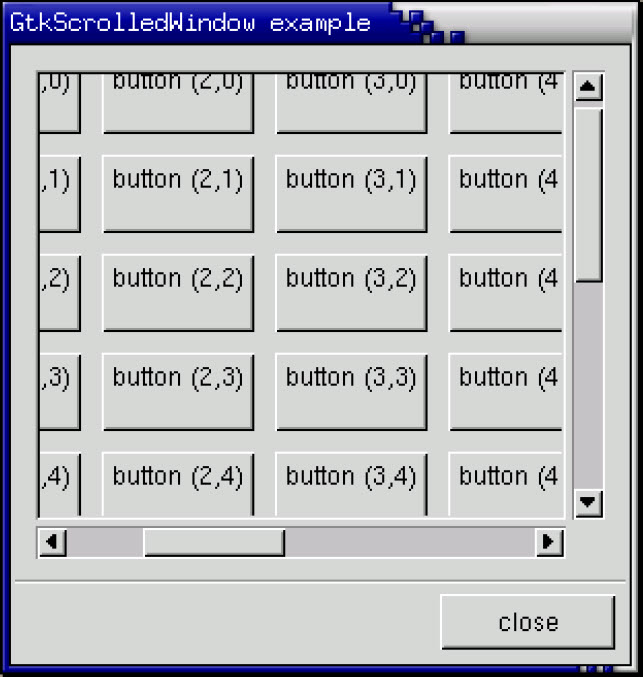
(* file: scrolledwin.ml *)
let main () =
(* Create a new dialog window for the scrolled window to be
* packed into. *)
let window = GWindow.dialog ~title:"ScrolledWindow example" ~width:300 ~height:300 ~border_width:0 () in
window#connect#destroy ~callback:GMain.Main.quit;
(* Create a new scrolled window *)
let scrolled_window = GBin.scrolled_window ~border_width:10
~hpolicy:`AUTOMATIC ~vpolicy:`AUTOMATIC ~packing:window#vbox#add () in
(* Create a table of 10 by 10 squares.
* Set the spacing to 10 on x and 10 on y *)
let table = GPack.table ~rows:10 ~columns:10 ~row_spacings:10 ~col_spacings:10
~packing:scrolled_window#add_with_viewport () in
for i = 0 to 10 do
for j=0 to 10 do
GButton.toggle_button
~label:("button ("^ string_of_int i ^","^ string_of_int j ^")\n")
~packing:(table#attach ~left:i ~top:j ~expand:`BOTH) ()
done
done;
(* Add a "close" button to the bottom of the dialog *)
let button = GButton.button ~label:"close" ~packing:window#action_area#add () in
button#connect#clicked ~callback:(window#destroy);
(* This grabs this button to be the default button. Simply hitting
* the "Enter" key will cause this button to activate. *)
button#grab_default ();
window#show ();
GMain.Main.main ()
let _ = Printexc.print main ()Try playing with resizing the window. You’ll notice how the scrollbars react. You may also wish to use the #misc#set_size_request method call to set the default size of the window or other widgets.